Abstract

Introduction: The management of Factor (F) VII deficiency is complex due to the lack of a clear correlation between FVII levels and the bleeding manifestations of the patients, with a variety of responses to the treatments. Additionally,the presence of FVII inhibitors may also occur. Thus, it is essential to be able to monitoring the hemostatic profile and the effect of the different therapies in each patient individually.
Our aim was to perform a personalized analysis of the coagulation status of patients with FVII deficiency and to evaluate their response to new potential therapies using five different coagulation tests.
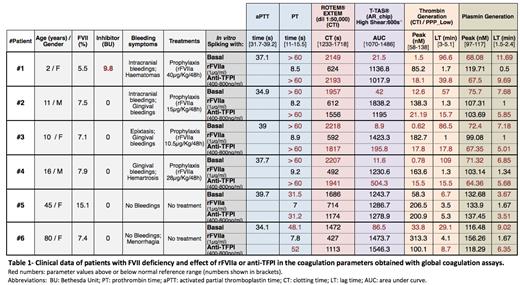
Methods: Six patients were included (clinical data in Table-1):4 with bleeding symptoms on prophylaxis with recombinant activated FVII (rFVIIa), one of them with FVII inhibitors; and 2 untreated patients without bleeding episodes. Blood samples obtained from patients on prophylaxis were collected predose.
Prothrombine time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)were tested using HemosIL ® RecombiPlasTin 2G, and SynthASil respectively.
Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM ®) was performed for monitoring the clot formation using blood with corn trypsin inhibitor (CTI) to inhibit contact activation and a low amount of Tissue Factor (TF) as trigger (dilution 1:50,000 of EXTEM reagent).
The thrombin generation (TG) was tested with the Calibrated Automated Thrombogram (CAT) system using platelet poor plasma (PPP) obtained from blood with CTI and activated with only 1 pM TF plus phospholipids (PPP-Low ®, Stago).
The plasmin generation (PG) was measured in citrated PPP using a comercial kit (Synapse).
The total thrombus-formation analysis system (T-TAS ®, Zacros) was conducted by loading CTI blood samples in AR-chips coated with collagen and thromboplastin for assessing thrombus formation mediated by the activation of the coagulation under flow conditions (High shear). The Area under the flow pressure curve (AUC) was calculated over 30 min after starting.
Effects of ex vivo spiking doses of factor replacement (rFVIIa) or non-factor replacement treatments (anti-TFPI, clone mAb2021, Creative Biolabs) were tested.
Results: aPTT values remained normal in all patients. FVII deficiency significantly affected PT and patients with more severe bleeding phenotype (patient #1, 2, 3, and 4) showed much longer PT values.
Similarly, ROTEM and T-TAS assays showed that FVII deficiency only caused an important delayed clotting time (CT) and very anomalous thrombus formation (AUC) in patients with severe bleeding symptoms.More prolonged lag time (LT) and an important decrease in the peak of thrombin and plasmin generation was also observed in the same patients (#1, 2, 3, and 4).
Patient #1 with FVII inhibitors presented a more affected hemostatic profile according to all the coagulation parameters obtained with the five different assays. In contrast, the patients #4 and #5 with absence of bleeding complications showed most of these values within the normal reference range obtained from healthy controls.
Concentrations of 1µg/ml (equivalent to 90 μg/kg) of the factor-replacement treatment rFVIIa, showed the normalization of the PT, the clotting time (CT), and the restoration of the thrombin and plasmin generation, and the regularization of the coagulation-dependent thrombus formation in all the patients.
In vitro spiking with anti-TFPI (400-800 ng/ml), an alternative non-factor replacement treatment,corrected the thrombus formation (AUC) defects under high shear flow observed in the patients, and produced a significant reduction of CT and LT, and increments of thrombin generation although less effectively than the factor replacement therapy.
Conclusions: All the global tests, performed with the described conditions in this study, were sensitive enough to show an abnormal hemostatic profile in the FVII-deficient patients with worst clinical symptoms, validating their use to monitor the risk of bleeding events and the responses to different treatments in this deficiency.
These assays may allow to monitoring more personalized treatments to these patients.
The results also pointed to the possibility that inhibition of TFPI might be useful for treatment of patients with FVII deficiency, opening the idea of its usage especially as an alternative therapy for patients with inhibitors.
Research funded by ISCIII-Fondos FEDER PI19/00772 and PI19/00631
Alvarez Román: Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sobi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Biomarin: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Octapharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novo-Nordisk: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Grifols: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; CSL-Behring: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. García Barcenilla: Roche: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau; SOBI: Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Speakers Bureau. Canales: Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; iQone: Honoraria; Sandoz: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria. Butta: CSL-Behring: Research Funding; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novo-Nordisk: Speakers Bureau. Jiménez-Yuste: Octapharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sobi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BioMarin: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; NovoNordisk: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Grifols: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal